Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) has changed psychology and neuroscience - the technology has made it possible to visualize the neural effects of both external stimuli, such as images or videos, and internal stimuli, such as thoughts or mental images. However, as all fMRI researchers know, fMRI signal is far from perfect, and is influenced by things like how much the participant moves and even how and when they breathe.
Improving the fMRI signal to noise ratio can happen during the scan, with motion reduction measurements like customized head molds or FIRMM software, or after the scan, with denoising techniques that take into account respiratory patterns. In one study, we demonstrated that customized head molds reduce motion in participants 7-28 years old. In a set of several other studies, we argued that respiratory patterns during a scan create noise, characterized different types of respiratory patterns, and demonstrated how certain breathing patterns are sex-biased, which could lead to sex-biased neural findings.
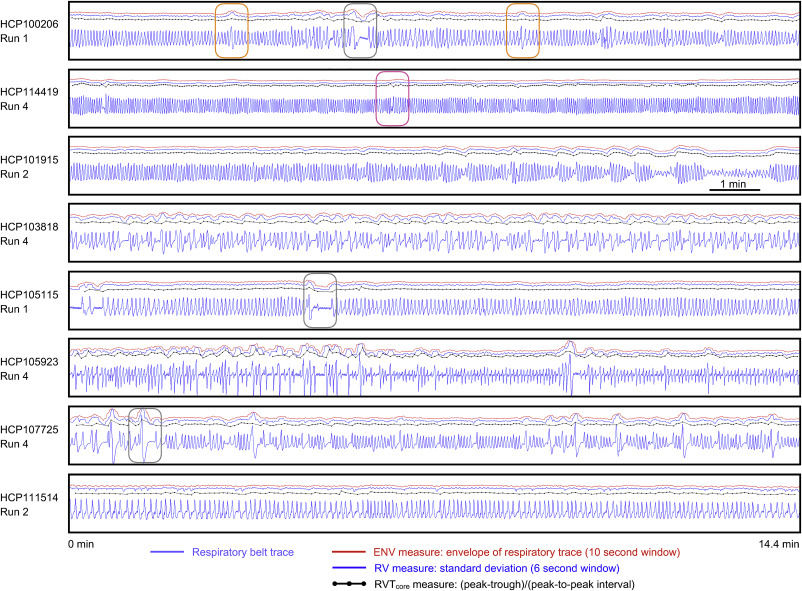 Different types of breathing patterns in Human Connectome Project subjects. From Power et al. 2020.
Different types of breathing patterns in Human Connectome Project subjects. From Power et al. 2020.
Related work
Lynch, C.J., Voss, H., Silver, B.M., Power, J.D. (2021). On measuring head motion and effects of headmolds during fMRI. Neuroimage. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.117494
Lynch, C.J., Silver, B.M., Dubin, M.J., Martin, A., Jones, R.M., Power, J.D. (2020). A prevalent, sex-biased respiratory pattern influences functional connectivity MRI in young adults. Nature Communications. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-18974-9
Power, J.D., Lynch, C. J., Dubin, M.J., Silver, B.M., Martin, A., Jones, R.M. (2019). Characteristics of respiratory measures in young adults scanned at rest, including systematic changes and “missed” deep breaths. Neuroimage. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.116234
Power, J.D., Lynch, C.J., Silver, B.M., Dubin, M.J., Martin, A., Jones, R.M. (2019). Distinctions among real and apparent respiratory motions in human fMRI data. Neuroimage. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.116041
Power, J.D., Silver, B.M., Silverman, M.R., Ajodan, E.L., Bos, D.J., Jones, R.M. (2019). Customized head molds reduce motion during resting state fMRI. Neuroimage. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.01.016